What is Dynamic Connectivity?
In computing and graph, a dynamic connectivity structure is a data structure that dynamically maintains information about the connected components of graph.
Dynamic Connectivity Problem
Given a set of N objects.
- Union command: connect two objects.
- Find/connected query: is there a path connecting the two objects?
Q. Is there a path connecting p and q?
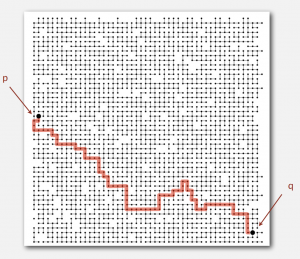
Union Find Data Type
The goal is to design an efficient data structure for union-find with two commands, union and connected. It can be implemented by two different algorithms, Quick Find and Quick Union.
Quick Find
This quick find algorithm is called eager algorithm to solve dynamic connectivity problem. The data structure includes an Integer array id[] of length N and we consider p and q to be connected iff they have the same id.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
id[i] = i; //set id of each object to itself
Union
To merge components containing p and q, change all entries whose id equals id[p] to id[q].
int pid = id[p];
int qid = id[p];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
if(id[i] == pid)
id[i] = qid;
Connected
Check if p and q have the same id.
return id[p] == id[q];
Java Implementation
public class QF
{
public int[] id;
public QF(int n)
{
id = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
id[i]=i;
}
}
public void union (int p, int q)
{
int pid = id[p];
int qid = id[q];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
if(id[i] == pid) {
id[i] = qid;
}
}
}
public boolean connected (int p, int q)
{
return id[p] == id[q];
}
}
Quick Union
It’s an algorithm for solving the dynamic connectivity problem, also called “lazy approach”.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i; //set parent of object at index i
Root
while (i != id[i]) i = id[i]; return i;
Union
To merge components containing p and q, set the id of p’s root to the id of q’s root.
int i = root(p); int j = root(q); id[i] = j;
Connected
Check if p and q have same root.
return root(p) == root(q);
Java Implementation
public class QuickUnionUF
{
private int[] id;
public QuickUnionUF(int N)
{
id = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
public int root(int i)
{
while (i != id[i]) i = id[i];
return i;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return root(p) == root(q);
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int i = root(p);
int j = root(q);
id[i] = j;
}
}






Be First to Comment